Comau developing automated system for battery recycling, second-life repurposing
Italian automation firm Comau has announced its continued participation in EU's Flexible Battery Dismantling 'Flex-BD' project for the second year, to help deliver a fundamental pillar on the path towards a truly circular economy.
Flex-BD is a robotized system that automates the entire process of dismantling worn-out electric batteries using a highly flexible, repeatable and standardizable process, the company claims.
Having validated the proof-of-concept, Comau has expanded the scope to include second life repurposing of automotive batteries. In doing so, the company, in collaboration with other partners within the EU EIT Manufacturing community, claims to be taking an important step towards greater sustainability within e-mobility.
RELATED: Glencore, FCC, and Iberdrola partner on Lithium-ion Battery circularity solutions
"Our work with the Flex-BD project leverages Comau's long standing automation expertise in the development of flexible, scalable and sustainable processes. By expanding our smart automation solution to include second life repurposing of high-power batteries, many of which have a residual capacity of up to 80 percent, Comau is making a concrete contribution to the realization of truly sustainable mobility", said Pietro Gorlier, CEO at Comau.
The company believes that Flex-BD represents a significant improvement to manual handling processes that often include repetitive and heavy tasks, along with exposure to potentially harmful substances. The system makes the recovery of battery modules and their components more efficient and sustainable while having a positive impact on workers' health and safety.
With second-life battery repurposing, on the other hand, the fully automated manipulation of low-charge batteries minimizes risks to both operators and the dismantling equipment, according to Comau. Unlike the materials recovery and recycling process, in which the battery is completely discharged and destroyed, second-life battery repurposing is done while maintaining a low but active battery charge.
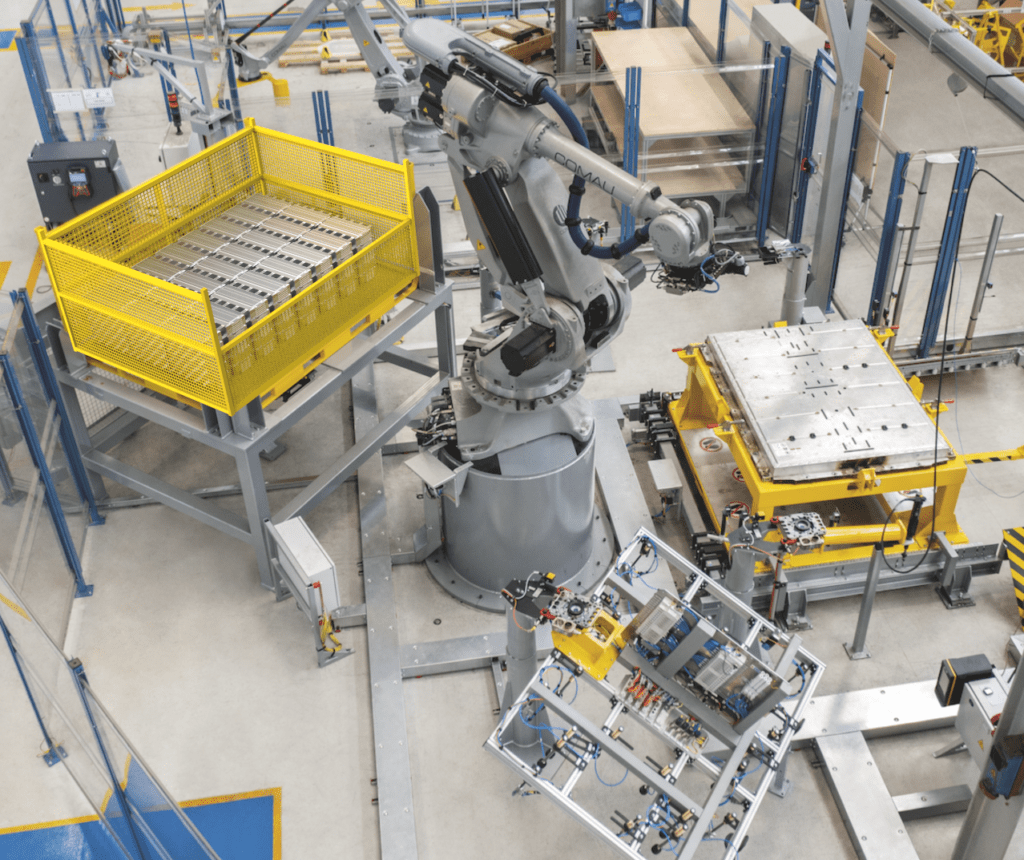
The battery packs are introduced into the specialized cell where a high-payload Comau NJ industrial robot automatically executes its path and changes its end-effectors based on the required application. In a typical recycling application, for example, the robot unscrews the battery cover, changes grippers to remove the cover, re-attaches the screwdriver to unscrew the modules and then using its gripper moves the pieces to a dedicated storage area.
RELATED: Enel X, MIDAC partner to develop Lithium Battery recycling plant in Italy
Interestingly, Flex-BD is designed around a highly flexible programming approach based on a reduced use of codes, state-of-the-art environmental perception techniques and the robot's reactive capacity, the entire dismantling cycle is defined through CAD. The use of 'LowCode' programming also allows operators to quickly and easily redefine the cycle with no need to reprogram the robot, claims Comau.
Comau adds that it is advancing green energy deployment beyond its expertise in automated manufacturing systems for batteries, electrical motors and drive units for EVs. This includes addressing several key technical and development aspects of the automation process for battery cell manufacturing, including process design and assembly of rechargeable cells, as well as the use of renewable energy and second-life strategies for automotive batteries.