Energy Storage Roundup 2021: Trends & takeaways
Energy storage is at the core of many technologies being deployed today to combat climate change. Post pandemic policies coupled with ambitious RE targets have continued to propel the growth of energy storage markets globally.
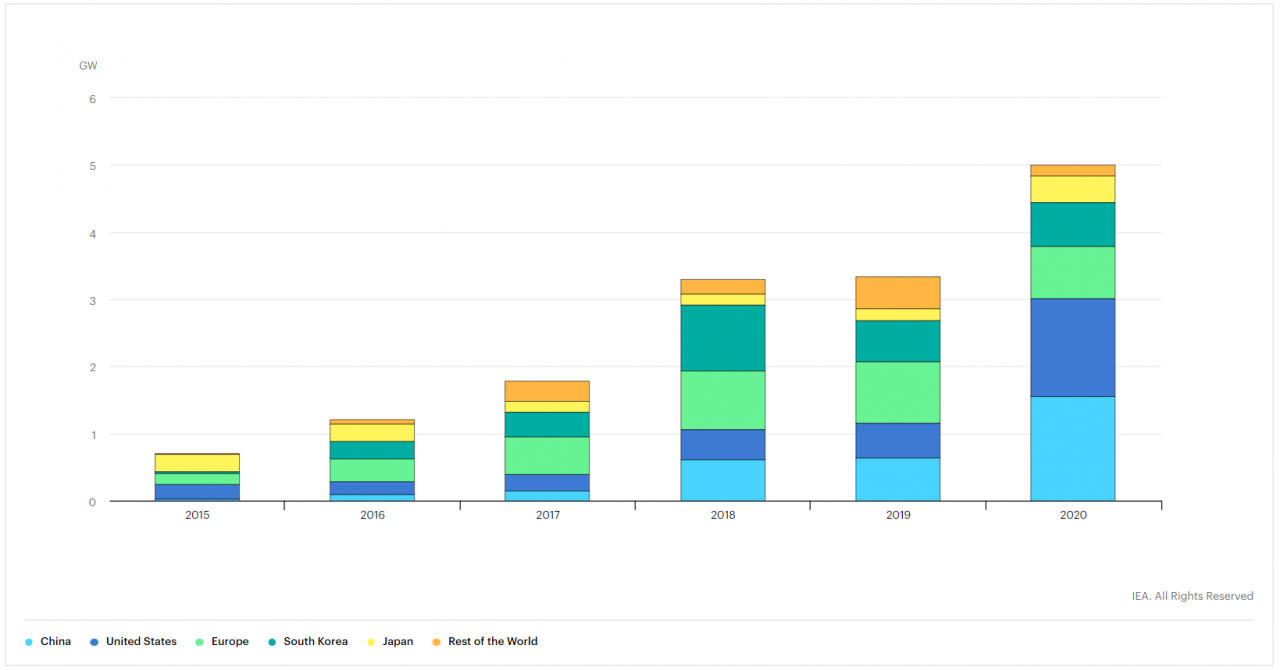
According to International Energy Agency's energy storage tracking report, globally 5GW of storage capacity was added in 2020, with China and the United States, each registering record gigawatt-scale additions. As per the report, the global energy storage market is led by China (1.6GW), the US(1.5GW), and Europe (0.8GW). Other main players in the market include Korea (0.7GW), Japan (0.4GW), the UK, and Australia.
Annual energy storage additions by country (2015-2021)
The two main drivers of growth of the energy storage sector globally are the integration of larger shares of variable renewable energy (VRE) into the grid, along with a shift towards e-mobility.
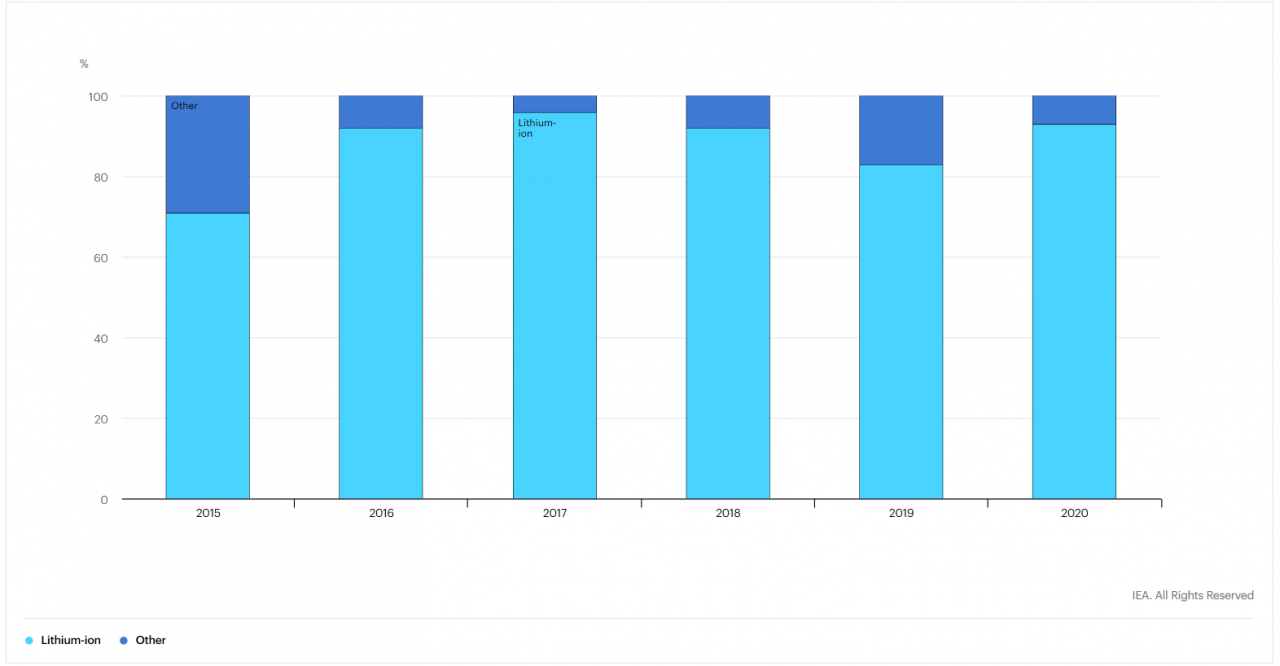
In terms of technology, data suggests lithium-ion battery storage continues to be the most widely used technology. As of 2020, Li-ion battery technology accounted for 93 percent of the total energy storage technology mix. Li-ion technology's dominant position is predicted to be augmented further, on account of the 'spill-overs' in EV deployments underway globally, in terms of innovations and cost reduction in mobility applications.
Other than batteries, many non-battery technologies such as compressed air and thermal energy storage are under development which can provide a longer dispatch duration compared to batteries. According to the report by research firm, Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) batteries will dominate the market at least until the 2030s; in large part due to their price competitiveness, established supply chain, and significant track record. If new technologies successfully outcompete Li-ion, then total uptake may well be larger.
Investments trends show that there is a growing appetite for investments in the energy storage sector today. IEA report indicates, overall investment in the battery storage industry increased by roughly 40 percent in 2020, to $5.5 billion. Spending on grid-scale batteries rose by more than 60 percent, owing to increased investments in renewables and an increasing number of hybrid auctions with storage. However, investments in behind-the-meter storage fell by 12 percent, largely because these investments are generally financed by households and small and medium companies, which were particularly hit hard by the COVID-19 crisis.
Enabling policies, changes in government regulations, and new projects announcements in the past year have spurred growth in global energy storage deployment, with steady progress in the sector.
NORTH AMERICA
In North America, specifically the United States, capacity additions from utility-scale projects more than quadrupled in 2020, led by two large projects in California. In December 2020, giving a significant boost to the clean energy industries, Congress approved a $900 billion COVID-19 relief bill that included a two-year extension of the solar investment tax credit benefitting energy storage deployments coupled with solar as well as the Better Energy Storage Technology Act, authorizing over $1 billion over five years to support the research and commercialization of a range of storage technologies.
In January 2021, the White House issued an executive order pledging to 100 percent clean electricity by 2035, and clean and zero-emission vehicles for Federal, State, local, and Tribal government fleets, including vehicles of the United States Postal Service.
Further, the world's largest battery energy storage system located at the Moss Landing Energy Storage Facility in California, US, became operational in January 2021. The project reportedly is the first 300MW Li-ion battery – comprising 4,500 stacked battery racks.
In July 2021, the Department of Energy (DOE) announced its Long Duration Energy Earthshot – a target to reduce the cost of grid-scale, long-duration energy storage by 90 percent within the decade. The target was announced as part of DOE's Energy Earthshots initiative, launched to accelerate breakthroughs of more abundant, affordable, and reliable clean energy solutions by 2030.
In Canada, steps are being taken by grid operators to recognize the value of energy storage systems including steps like the pilot grid services tender by Alberta's grid operator, and the publication of interim market rules and manuals for energy storage's participation in energy markets by the Ontario IESO.
In November, the Canadian Renewable Energy Association (CanREA), a trade group with 300+ member organizations outlined five priority actions that would accelerate Canada's transition to low carbon energy, including specific moves to support the deployment of energy storage. The document urged that the regulatory and policy landscape be radically altered to enable the considerable development of renewable energy and energy storage.
LATIN AMERICA
In Latin America, an ambitious renewable energy target is predicted to drive growth in the energy storage sector. A new regional initiative coordinated by the Latin American Energy Organization (OLADE) sets a regional goal of reaching at least 70 percent of renewable energy in electricity by 2030.
The research from Wood Mackenzie, in its recent forecast, reports that the Latin American market will reach 1GW/ 2.5GWh of cumulative capacity by 2025 and 5GW/12.3 GWh by 2030, with an average of 575 MW of annual installations throughout the forecast period. The analysis notes storage projects in the region so far have been focused on ancillary services or micro-grids, but the future opportunities will come from commercial and industrial contracts for hybrid projects and technology auctions to be held in Colombia and Chile.
EUROPE
In Europe, the utility-scale installations dropped but they were offset by a strong expansion in residential installations. Germany is currently Europe's leading market where behind-the-meter installations nearly doubled.
Earlier this month, it was reported that the European battery maker Northvolt, has gone all out to meet the 2021 launch goal for the battery plant. The Li-ion battery plant was the first to be built in the European Union by Northvolt and it is set to be a launchpad for a regional battery champion that can compete not only with battery behemoth, Tesla, but also major Asian suppliers including Panasonic, LG Chem, and CATL. Northvolt plans to produce enough batteries to power over 1 million EVs annually from its Swedish facility based in Skelleftea, and later, supply to other sectors such as industrial machinery and ferries.
Northvolt has raised more than $6.5 billion in funding from investors including Volkswagen Group, the European Commission, and Spotify founder Daniel Ek as well as contracts worth over $27 billion from automakers.
In Great Britain, the National Grid Electricity System Operator is conducting a weekly auctioning trial and launched its Dynamic Containment frequency response service in October 2020, providing significant opportunities for storage with fast response requirements mostly satisfied by batteries. National Grid data showed that as of Jan. 29, 2021, ~396MW of battery storage capacity was contracted.
MIDDLE EAST & NORTH AFRICA
In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) the mid-and long-term renewable energy targets for MENA countries – which range from 15 percent to up to 50 percent of total electricity generation – show that governments are committed to increasing the share of renewables in the energy mix along with battery storage systems.
Some of the current technologies being used for energy storage in MENA include pumped hydro storage (PHS) and electrochemical energy storage – mainly sodium-sulfur and Li-ion batteries. Most of the planned and operational projects are in the Gulf Corporation Council (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman), North Africa (Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia), with several projects in the Levant – mainly in Jordan, Iraq, and Lebanon.
As per reports, there are 30 energy storage system projects planned in MENA between 2021-2025 with a total capacity/energy of 653 MW/3,382 MWh – of which 24 projects are for VRE integration and grid firming. The share of batteries of the total energy storage landscape in MENA is expected to jump from the current 7 percent to 45 percent by 2025.
ASIA
IEA reports that capacity additions in China more than doubled in the year 2020. This strong growth was driven by projects for renewable energy integration and the commissioning of delayed projects. In July 2021, China's State planner announced it aims to install more than 30GW of new energy storage capacity by 2025 (excluding pumped hydro), as part of efforts to boost renewable power consumption while ensuring stable operation of the electric grid system. IEA highlights, this target would mean a nearly 10-fold increase in its installed capacity as of 2020.
In Korea, deployments rose 6 percent last year after a steep drop between 2018 and 2019, as the government subsidies that promoted the growth of the energy storage market were phased out. The country which is home to two top lithium-ion manufacturers, LG Chem and Samsung SDI, hopes to get 10 percent renewable electricity in 2023 and 20 percent by 2030.
IEA report indicates that Japan's strong growth in behind-the-meter storage installations continued last year, reaching nearly 300 MW in 2020. In August 2021, Tesla joined hands with Japanese companies to build an energy storage facility in Northern Japan. Tesla collaborated with Japanese power retailer Envision to build the energy storage facility connected to the grid with a 6,095kWh capacity that could power about 500 homes.
In India, in October 2021, the Power Ministry announce its aim to bring out a comprehensive policy on energy storage that would broadly focus on regulatory, financial, and taxation, demand management, and technological aspects to speed up the implementation of storage capacity.
In May 2021, the Union cabinet approved the ₹18,000 crore Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for battery storage. The PLI scheme 'National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage' for building the manufacturing capacity of 50 GWh of ACC and 5 GWh of 'Niche' ACC in India.
In December 2021, the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) awarded Tata Power to build a 100MW EPC solar project along with a 120MWh utility-scale battery energy storage system. Tata Power is currently executing another solar project of 50MW with BESS of 50MWh battery storage in Leh.
The Indian government has plans to set up a 14GWh grid-scale battery storage system at the world's largest renewable energy park at Khavda, Gujarat and intends to invite bids for the largest global tender for setting up a 13GWh grid-scale battery storage system in Ladakh.
Further, it has plans to call bids for setting up around 4GWh of the grid-scale battery storage system at the regional load dispatch centres. The State-run NTPC Ltd has floated a global tender for setting up 1GWh grid-scale battery storage system.
India Energy Storage Alliance (IESA) estimates the market for energy storage would grow to over 300GWh during 2018-25.
AUSTRALIA
Australia remains a key market for behind-the-meter storage, but utility-scale deployments are expected to dominate over the next several years. The country had planned to add 1.2GWh of energy storage capacity in 2020, more than double the 499MWh installed in 2019 (Wood Mackenzie) – increasing the country's cumulative storage capacity to 2.7GWh.
Some landmark projects in the region include the Hornsdale Power Reserve, the world's largest operating battery developed by French renewables developer Neoen. It is a 100MW/ 129MWh Tesla big battery project in South Australia. Neoen, in April 2020, had announced plans to develop another massive battery storage system near the Australian city of Geelong – a 600MW battery storage facility dubbed as 'Victoria big battery'.
General Electric (GE) also won its largest battery deal so far to support the 200MW Solar River Project in South Australia, which will be combined with a 100MW – 300MWh GE Reservoir grid storage system. The project already is slated to start generating power by 2021.
CEP Energy has announced plans for a 1,200 MW battery in NSW's Hunter Valley to be built in stages, with the first to be delivered by 2023. The A$2.4 billion (US$1.85 billion) project will eclipse California's Moss Landing Energy Storage Facility to become the world's largest battery energy storage system. CEP has plans to be part of a network of four big grid-scale batteries across the country with a total capacity of 2,000MW.